How Is Cytokinesis In Plant Cells Different From Cytokinesis In Animal Cells?
Cytokinesis is the division of the cytoplasm into two daughter cells. During the cell cycle of eukaryotes, karyokinesis is followed by the cytokinesis. This means that the segmentation of the cytoplasm takes identify after the completion of the segmentation of the nucleus. All the same, the cytokinesis or the division of the cytoplasm does not happen in the same way in plant and animal cells. This commodity volition explain the difference in institute and animal cytokinesis and the cause is for this divergence.
This article looks at,
1. What Happens During Cytokinesis
2. Plant Cell Cytokinesis
3. Brute Cell Cytokinesis
four. How is Cytokinesis Different in Plants and Animals
What Happens During Cytokinesis
During cytokinesis, duplicated genetic material at the reverse poles is separated into two daughter cells forth with the one-half of the jail cell's cytoplasm, containing 1 ready of its organelles. The separation of the duplicated genetic material is ensured by the spindle apparatus. The number of chromosomes, as well as the number of chromosome sets of a daughter prison cell, should be equal to those of the female parent cell in guild to the girl cells to be the functional copies of the parent cells. This procedure is called the symmetrical cytokinesis. On the opposite, during oogenesis, the ovum consists of nearly all the organelles and the cytoplasm of the precursor germ cell gonocytes. Yet, cells of the tissues like liver and skeletal muscle omit the cytokinesis by producing multi-nucleated cells.
The main difference betwixt establish cell and animal cell cytokinesis is the formation of new cell wall surrounding the daughter cells. Plant cells form a cell plate between the 2 girl cells. In brute cells, a cleavage furrow is formed between the two daughter cells. In mitotic partitioning, afterward the completion of the cytokinesis, daughter cells enter into the interphase. In meiotic division, produced gametes are used for the completion of the sexual reproduction after the completion of cytokinesis past fusing with the other type of the gametes in the same species.
Plant Cell Cytokinesis
Plant cells ordinarily consist of a cell wall. Therefore, they form the cell plate at the eye of the parent jail cell, in order to dissever two daughter cells. Formation of the cell plate is shown in figure i.
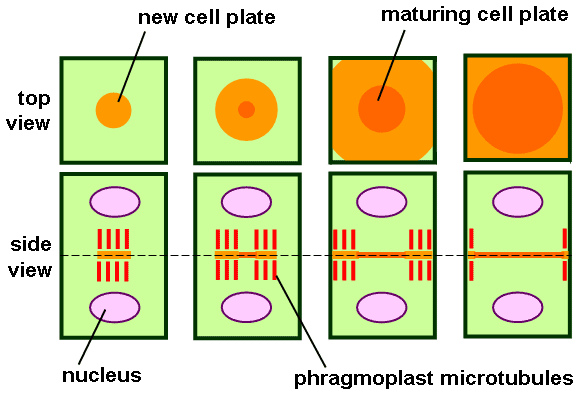
Figure 1: Jail cell Plate Germination
Process of Prison cell Plate Formation
The cell plate formation is a v step process.
Phragmoplast Formation
Phragmoplast is microtubule array, supporting and guiding the jail cell plate germination. The microtubules which are utilized for the formation of the phragmoplast are the remnants of the spindle.
Trafficking of Vesicles and Fusion with Microtubules
Vesicles containing proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids are trafficked into the mid zone of the phragmoplast by the microtubules since they are required for the formation of the jail cell plate. The source of these vesicles is the Golgi apparatus.
Fusion and transformation of the membrane tubules into the membrane sheets Widened microtubules
Widened microtubules laterally fuse with each other in order to form a planar canvass which is referred to as the jail cell plate. Other prison cell wall constituents along with cellulose deposit on the cell plate bulldoze it to further maturation.
Recycling of the cell membrane materials
Unwanted membrane materials are removed from the cell plate by clathrin-mediated endocytosis.
Fusion of the cell plate with the existing prison cell wall
The edges of the cell plate are fused with the existing parental cell membrane, physically separating the two daughter cells. Most of the time, this fusion occurs in an asymmetric manner. Just, strands of the endoplasmic reticulum is establish passing through the newly formed prison cell plate, which behaves every bit the precursors of the plasmodesmata, a type of cell junctions constitute in plant cells.
Different cell wall components like hemicellulose, pectins, arabinogalactan proteins, which are carried past the secretary vesicles, are deposited on the newly formed cell plate. The most abundant component of the prison cell wall is cellulose. First, callose is polymerized by the callose synthase enzyme on the prison cell plate. As the prison cell plate fuses with the existing cell membrane, callose is somewhen replaced by the cellulose. Center lamella is generated from the jail cell wall. Information technology is a glue-like layer, consisting of pectin. The two next cells are bound together by the heart lamella.
Fauna Cell Cytokinesis
The cytoplasm division of the animate being cells begins after the separation of the sister chromatids during the anaphase of the nuclear segmentation. Animate being jail cell cytokinesis is shown in figure two.
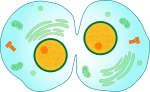
Figure 2: Animal Cell Cytokinesis
Animal Cell Cytokinesis Procedure
Animal cell cytokinesis takes identify through four steps.
Anaphase Spindle Recognition
The spindle is recognized past the CDK1 activeness declines during the anaphase. Then, microtubules are stabilized in order to grade the central spindle or the spindle midzone. Not-kinetochore microtubules form bundles in between the two opposite poles of the parent cell. Humans and C. elegans require the formation of central spindle in order to comport out an efficient cytokinesis. The declined activity of CDK1, dephosphorylates the chromosomal passenger complex (CPC), translocating the CPC to the central spindle. The CPC locates at the centromeres during the metaphase.
The CPC regulates the phosphorylation of cardinal spindle component proteins similar PRC1 and MKLP1. The phosphorylated PRC1 forms a homodimer which binds in the interface between the antiparallel microtubules. The binding facilitates the spatial arrangement of the microtubules on the central spindle. The GTPase activating protein, CYK-iv and phosphorylated MKLP1 form the centralspindlin circuitous. The centralspindlin is a college-society cluster which is bound to the primal spindle.
The multiple central spindle components are phosphorylated in social club to initiate the self-assembly of the primal spindle. The central spindle controls the position of the cleavage furrow, maintains the membrane vesicle commitment to the cleavage furrow and controls the midbody formation at the end of the cytokinesis.
Division Airplane Specification
The specification of the division plane tin can occur through three hypothesis. They are astral stimulation hypothesis, central spindle hypothesis, and astral relaxation hypothesis. Two redundant signals are sent past the spindle, positioning the cleavage furrow to the cell cortex, 1 from the fundamental spindle and the other from the spindle aster.
Actin-Myosin Band Assembly and Wrinkle
The cleavage is driven by the contractile band formed by actin and a motor protein, myosin-II. In the contractile ring, both cell membrane and jail cell wall grow into the cell, pinching off the parent cell into two. Rho protein family regulates the formation of the contractile ring in the middle of the cell cortex and its wrinkle. The RhoA promotes the formation of the contractile ring. In addition to actin and myosin II, the contractile ring consists of scaffolding proteins like anillin, which binds with CYK1, RhoA, actin and myosin II, linking equatorial cortex and the key spindle.
Abscission
The cleavage furrow ingresses to form the midbody structure. The diameter of the actin-myosin ring at this position is around ane-2 μm. The midbody is completely cleaved in a process called abscission. During abscission, intercellular bridges are filled with antiparallel microtubules, the cell cortex is constricted and plasma membrane is fashioned.
Molecular signaling pathways ensure the true-blue separation of the genome between the two girl cells. The animal cell cytokinesis is powered by Type II Myosin ATPase in gild to generate the contractile forces. The timing of the fauna cytokinesis highly regulated.
How is Cytokinesis Different in Plants and Animals
The segmentation of the cytoplasm is referred to as cytokinesis. The primary divergence between plant and animal cell cytokinesis is the formation of a jail cell plate in plant cells, rather than the germination of the cleavage furrow in animal cells. The departure between institute and animate being cell cytokinesis is shown in figure 3.

Effigy 3: Difference Between Animal and Plant Cytokinesis
Animal cells practice non possess a cell wall. Thus, only the jail cell membrane is divided into 2, forming new cells past deepening a cleavage through a contractile band in the eye of the parent cell. In plant cells, a prison cell plate is formed in the centre of the parent cell with the aid of microtubules and vesicles. Vesicles are fused with microtubules, forming a tubular-vesicular network. The deposition of cell wall components leads to the maturation of the cell plate. This cell plate grows towards the cell membrane. Therefore, an creature cell's cytoplasmic division begins in the edges of the cell (centripetal) and plant cell's cytoplasmic division begins at the middle of the cell (centrifugal). Thus, midbody germination can exist identified only in the fauna cell cytokinesis. The cytokinesis of plant cells begins at the telophase of the nuclear partition and animate being cell cytokinesis begins at the anaphase of the nuclear division. Animal jail cell cytokinesis is tightly regulated by signal transduction pathways. It as well requires ATP for the contraction of actin and myosin proteins.
Reference:
i. "Cytokinesis". En.wikipedia.org. N.p., 2017. Web. 7 Mar. 2017.
Image Courtesy:
ane. "Phragmoplast diagram" by BlueRidgeKitties (CC BY ii.0) via Flickr
2. "Mitotic Cytokinesis"By MITOSIS_cells_secuence.svg: LadyofHatsderivative work: Matt (talk) – MITOSIS_cells_secuence.svg (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia three. "Algae cytokinesis diagram" by BlueRidgeKitties (CC BY 2.0) via Flickr

Source: https://pediaa.com/how-is-cytokinesis-different-in-plants-and-animals/
Posted by: frazieroffily.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How Is Cytokinesis In Plant Cells Different From Cytokinesis In Animal Cells?"
Post a Comment