How Are Animal And Plant Cells Similar How Are They Different Explain
A Cell is the smallest structural and functional unit of life. Typically, there are two types of cells, i.e., prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotes are pre-existing cells and eukaryotes evolved afterwards. Both plants and animals cells are eukaryotes. Both share so many structural and functional similarities yet contrasting characteristics.
A plant cell structure is very similar to that of the brute cell, the ii types of cells contain many of the same organelles. These organelles carry out the same functions in both types of cells. Aside from common organelles, establish and animal cells are very unlike. Constitute cells are very unique because of the presence of three additional structures. These structures (a cell wall, vacuoles, and plastids) are important to a constitute'southward power to function.
What is a Plant Cell?
Plant cells vary considerably in size, shape and structure. It is, therefore, difficult to present a general moving picture of plant cells. Typically, plant cells are cubic or rectangular in shape and a lot bigger than creature cells in structure. They are very unique because of the presence of three additional structures. These structures (cell wall, vacuoles, and plastids) are important to a found'due south ability to role.
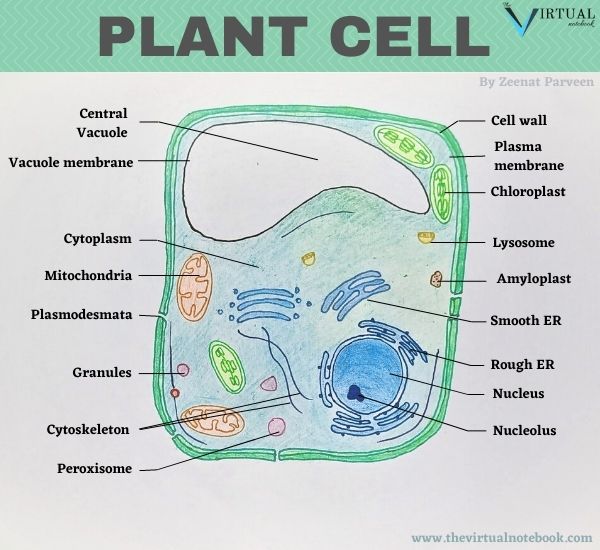
The cytoplasm of plant cells is an aqueous medium of different viscosity and composition which contains membrane-bound bodies known as organelles. Also embedded in the cytosol are chloroplasts (plastid), mitochondria, ribosomes, Golgi appliance, peroxisomes, glyoxysomes, spherosomes, microtubules and microfilaments (role of the cytoskeleton).
What is an Fauna jail cell?
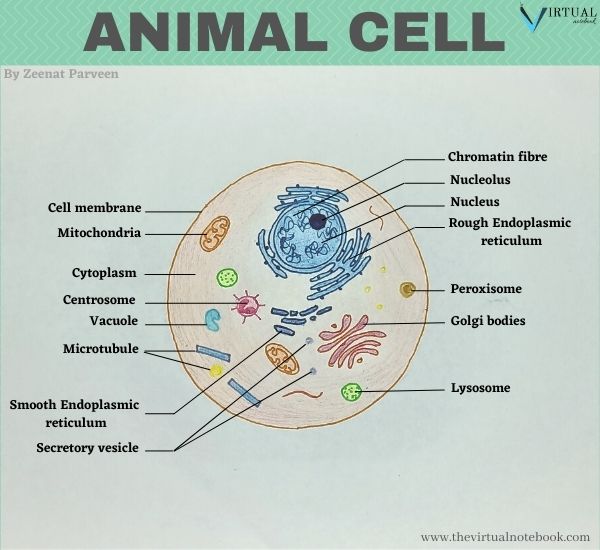
Like plant cells, they are besides eukaryotic cells but lack an outer jail cell wall. They have a true membrane-bound nucleus forth with other cellular content. Animal cells are more often than not smaller in size as compared to found cells and may contain more than 1 vacuole.
Similarities between establish cell and brute prison cell
- Ribosomesouth: bothe cells accept ribosomes.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum: it is nowadays in both establish and fauna cells.
- Style of reproduction: both have like reproduction process of Mitosis and Meiosis.
- Both have cell membrane or plasma membrane
- institute cell and fauna jail cell take well defined nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondria, peroxisomes, vacuoles and Dna every bit their genetic cloth.
- Cytoskeleton Arrangement: both cells have well-develped cytoskeleton system.
Difference betwixt Constitute prison cell and Animate being cell
Morphologically, animal cells are smaller than constitute cells. They both take differences in their shape and sizes. Lets discuss various differences in detail.
What is found/animal cells?
Plant cell: Plant cells have a membrane-bound nucleus and vary profoundly in size, grade, structure, and function. Some are measured in micrometres, others in millimetres, and withal others in centimetres (fibres in certain plants).
Animal jail cell: An creature fall under the category of eukaryotic prison cell that lacks a cell wall and has a true, membrane-bound nucleus forth with other cellular organelles.
Plant cell vs creature cell organelles
Although the establish cell structure is very similar to that of the animal cell, the 2 types of cells contain many of the aforementioned organelles. These organelles acquit out the same functions in both types of cells. Aside from common organelles, plant and animate being cells are very different.
Establish cells are very unique considering of the presence of iii additional structures. These structures (a cell wall, vacuoles, and plastids) are of import to a plant'southward ability to office.
A plant/fauna cell has diverse cell organelles:
- Prison cell wall: It is the outermost purlieus of the eukaryotic plant cell. Due to the presence of cell wall, the structure of institute cell is more than rigid than animal jail cell. However, it is absent in animal cells.
- Cytoplasm: It is thick semi-fluid substance of the cell lying just below the cell membrane. It is present in both plant and beast cells.
- Plasma Membrane: It separates the interior of the prison cell from the ouside environment and nowadays between the prison cell wall and the cytoplasm. Information technology is present in both types of prison cell.
- Nucleus: It contains the blueprint that make up one's mind the structure and function of both plant cell and animal jail cell. Information technology is present in both types of cells. Although, it is the largest organelle nowadays in animate being cell while not a example plant prison cell.
- Ribosomes: They are protein builders/synthesizers of the cell. They are present in both cells.
- Cytoskeleton: information technology is a network of interconnected poly peptide filaments and tubules that extends from the plasma membrane to the nucleus in both animal and institute cells. In animal cells, Microtubules (of cytoskeleton) unremarkably radiate from the centrosome located almost the nucleus. On the other hand, they are more nigh the plasma membrane in found cells.
- Golgi complex: It is an organelle that sorts and modifies proteins and lipids (fats). They are nowadays in both the cells. These small connected units are called dictysomes in institute cells instead of golgi bodies.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum: it is an organelle that contain a series of flattened sacs within the cytoplasm. Its primary function is to modify and synthesis proteins in eukaryotic cells. Once more, information technology is nowadays in both institute prison cell and anima cell.
- Plastids: These are double membrane-bound organelles that testify nifty variations in shape, size and numbers. They are just present in plant prison cell while absent in animate being cells.
- Mitochondria: They are likewise double membrane structures and are oftern called the ability firm of the cell. Plant cell contain fewer mitochondria than animal cells.
- Vacuoles: Together with the presence of plastids and cell wall, the vacuole is one of the three characteristics that distinguish constitute cell from an fauna prison cell. Vacuoles are present in both the jail cell only vacuole in plant cell is larger than vacuoles in animal cell. Vacuole is likewise permanent in found cell whereas it is temporary in animalc cell.
Size
Establish cells are much larger than brute cells. The normal range for an beast jail cell varies from 10-xxx μm while that for a constitute cell stretches from x-100 μm.
Shape
Constitute cells show a wide range of shapes and internal structures, depending on their function. Typically, plant cells are cubic or rectangular in shape and a lot bigger than creature cells in structure. On the other hand, animal cells are irregular due to the absenteeism of a jail cell wall.
Cilia and flagella
Cilia: they are small, slender, hair-like structures present on the surface of eukaryotic cells. They are of two types: Motile and non-motile.
Flagella: It is also a lash-similar construction that protrudes from the prison cell body.
Cilia and flagella aid in the locomotion and sensing of the extracellular environments. They are present in animal cells whereas absent in plant cells.
Plasmodesmata
These are pores or channels nowadays in the cell wall of establish cells. They link adjacent plasma membranes and cytoplasm. Also, they assistance in the communication and send of materials across plant cells. Every bit they are only present in the cell wall, they are unique to constitute cells. Hence, absent in animal cells.
Plant prison cell VS animal cell diagram
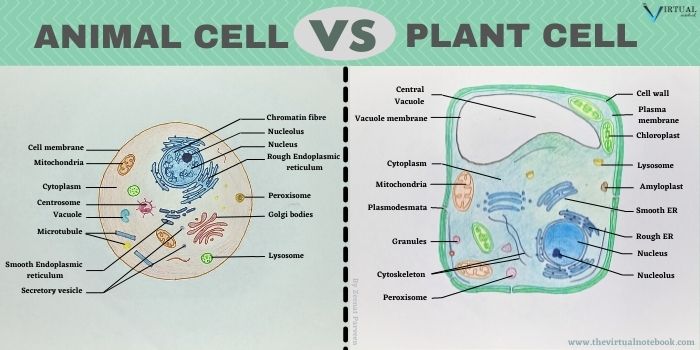
Institute prison cell VS animal cell table
| CHARACTERISTICS | ANIMAL Cell | PLANT CELL |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | These are eukaryotic prison cell that have plasma membrane as their outermost organelle. | They are also eukaryotic cell that have jail cell wall as their outermost membrane forth with other unlike organelles. |
| Kingdom | Animalia | Plantae |
| Size | smaller. Size of cell varies from 10-30 μm. | Larger than animate being cells. cell varies from 10-100 μm. |
| Shape | They are round to irregular in shapes | They vary greatly in size, form, structure, and function. Plant cells are cubic or rectangular in structure. |
| Cell wall | it is absent. | Cellulose cell wall is present. |
| Effect of hypotonic solution | Animal cells can hands bursts when placed in hypotonic solution considering of the lack of a cell wall | They exercise not flare-up in a hypotonic solution due to the presence of a cell wall. |
| Largest organelle | Nucleus | Plastids |
| Golgi bodies | Well developed Golgi bodies are are that have two cisternae. | It is present in the grade of units known equally dictyosomes |
| Centriole | Present | Absent in higher plants simply some lower plants do take centrioles. Case: Algae, chlamydomonas |
| Mode of nutrition | Heterotrophic | Autotrophic |
| Ability to brand ain nutrient | Equally they are heterotrophic, they cannot produce their own food. | They can synthesize their own food. |
| Chloroplast | Absent | Present. Information technology enables plants to perform photosynthesis. |
| Vacuole | Present merely smaller than institute cell. | It is as well present but much larger than animate being prison cell. |
| Nature of vacuole | Numerous and temporary | 1, permanent and central vacuole is nowadays in mature plant cell. |
| Cell Membrane | It is the outermost membrane in animal prison cell that encloses the cellular contents. | Information technology is present beneath the cell wall in plant cells. |
| Cytoplasm | Information technology houses all the cell organelles. | It houses most of the cell organelles. |
| Centrosomes | Present | Absent |
| Plastids | Absent | Present They provide color to the plants and helps in trapping the light energy. |
| Cilia | It is present in certain cells. Example: epithelium lining of respiratory tract. | Absent |
| Flagella | Certain animal cells have flagella. Example: spermatozoa | It is absent-minded. |
| Mitochondria | They are present in abundant | They are as well nowadays in constitute jail cell simply their number is much lower than animal cells. |
| Plamodesmata | Entirely absent in animal cells. | Present in the cell wall of plant cell. |
| Microtubules | Microtubules (of cytoskeleton) usually radiate from the centrosome located most the nucleus. | they are more than near the plasma membrane in constitute cells. |
| Nucleus | Present. It is the largest organelle in fauna cells | Present. It is not the largest organelle in found cell. |
| Lysosomes | Present | Rarely present as the found vacuole and the Golgi bodies handle molecule deposition of waste cellular products. |
| Endoplasmic reticulum | it is present | present |
| Microvilli | Nowadays. Example: intestinal lining of digestive system | It is absent-minded |
| Endosomes | These are membrane-jump vesicles present in the cytoplasm of all the animate being cells. | Nowadays. Constitute endosomes have different structural and functional organizations as compared to animal cells. |
References
Cell biology: organelle structure and office by David East. Sadava. Page no.241-263, page no. 295-303, chapter 9
Prison cell biology by David E. Sadava; CBS publisher; from page no. 213-225
Cell and molecular biological science by Prakash S. Lohar; MJP Publishers; from folio no. sixteen-eighteen, 96-98, 115-117, 122-130
The cell: A molecular approach by Geoffrey M. cooper, fourth edition
Cell biology, genetics, molecular biological science, development and ecology past P.S Verma and 5.Chiliad. Aggarwal; page no. 146-148, 186-190
Essau'due south Plant Beefcake, third edition, affiliate: The Protoplast: Plasma Membrane, Nucleus, and Cytoplasmic Organelles
Constitute Biochemistry edited by P.Chiliad. Dey and J.B. Harborne, chapter no. i: The plant, the cell and its molecular component
Essentials of biological science, 5th edition by Sylvia South. Mader and Michael Windelspecht
Lehninger; principles of biochemistry by Michael M. Cox and David East. nelson, page no. 246,247, 795-96.
https://byjus.com/biology/beast-cell/
https://byjus.com/biology/difference-between-establish-jail cell-and-animal-prison cell/
https://biologydictionary.cyberspace/animal-cell/
https://www.thoughtco.com/all-about-animate being-cells-373379
https://microbenotes.com/plant-cell-vs-animate being-cell/
https://chemdictionary.org/brute-jail cell/
Source: https://www.thevirtualnotebook.com/plant-cell-vs-animal-cell-similarities-differences/
Posted by: frazieroffily.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How Are Animal And Plant Cells Similar How Are They Different Explain"
Post a Comment